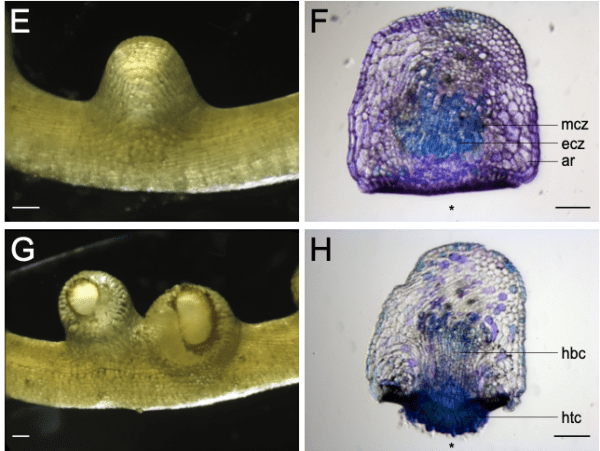
The development of the infection organ of the parasitic angiosperm genus Cuscuta is a dynamic process that is normally obscured from view as it happens endophytically in its host. We artificially induced haustoriogenesis in C. campestris by far-red light to define specific morphologically different stages and analyze their transcriptional patterns. This information enabled us to extract sets of high-confidence housekeeping and marker genes for the different stages, which were then validated in a natural infection setting on a compatible host. This study provides a framework for more reproducible investigations of haustoriogenesis and the processes governing host-parasite interactions in shoot parasites, with C. campestris as a model species.